Norepinephrine and the Overdrive Effect: How Burnout Disrupts Your Focus and Energy
Do you feel constantly "on edge," yet drained at the same time? Burnout creates this paradox by hijacking your brain's norepinephrine system.
Norepinephrine, also known as noradrenaline, is the brain's "fight or flight" chemical. It keeps you alert, helps you focus, and primes your body to handle challenges. But when chronic stress or burnout strikes, this system becomes unbalanced, leading to anxiety, poor concentration, and physical exhaustion.
This article explains the role of norepinephrine in your brain, how burnout disrupts it, and how you can help your system recover.
What Is Norepinephrine?
Norepinephrine is both a neurotransmitter and a hormone. It plays a crucial role in:
Arousal and alertness
Attention and focus
Mood regulation
Stress response
Energy and motivation
Norepinephrine is primarily produced in a small brain region called the locus coeruleus (located in the brainstem) and spreads to many brain areas, including the cerebral cortex, amygdala, hippocampus, and spinal cord.
When healthy, this system helps you respond effectively to sudden challenges. It increases heart rate, releases glucose for energy, and sharpens mental focus. But prolonged stress keeps it switched on too long.
Norepinephrine Pathways in the Brain
Norepinephrine travels through several key pathways in the brain, all originating from the locus coeruleus. These pathways are critical for regulating focus, attention, arousal, and emotional responses:
1. Locus Coeruleus to Prefrontal Cortex
This pathway controls executive functions like decision-making, attention, and working memory. When norepinephrine levels are optimal, it enhances focus and mental clarity.
2. Locus Coeruleus to Amygdala
This pathway influences the processing of emotions, especially fear and anxiety. Overactivation due to chronic stress heightens emotional reactivity.
3. Locus Coeruleus to Hippocampus
This connection supports learning and memory formation. Disruptions from burnout can lead to forgetfulness and impaired memory.
4. Locus Coeruleus to Spinal Cord
This pathway helps modulate motor function and sympathetic nervous system responses like heart rate and blood pressure.
Together, these pathways orchestrate the body’s fight-or-flight response. However, in burnout, chronic overactivation of these circuits leads to emotional dysregulation, poor focus, and energy imbalances.
How Burnout Affects the Norepinephrine System
Burnout transforms norepinephrine from a helpful signal into a source of distress. Here’s how:
1. Chronic Overactivation
Prolonged stress causes the locus coeruleus to overproduce norepinephrine. This creates a constant state of hyper-alertness. It’s like having an internal alarm system that won’t shut off.
2. Impaired Regulation
With time, your body becomes less able to regulate norepinephrine levels, leading to hypersensitivity to even minor stress triggers. Everyday situations begin to feel overwhelming.
3. The Exhaustion Phase
Eventually, your system may become depleted or desensitized. This results in fatigue, lethargy, and apathy all of which are classic signs of burnout.
4. Increased Amygdala Activity
Chronic stress enhances norepinephrine signaling in the amygdala, the brain’s fear center, making anxiety and fear responses much stronger. This can also contribute to panic attacks.
5. Disruption of Sleep-Wake Cycles
Excess norepinephrine can disturb the body's natural circadian rhythm, causing sleep difficulties such as insomnia, restless sleep, or frequent waking.
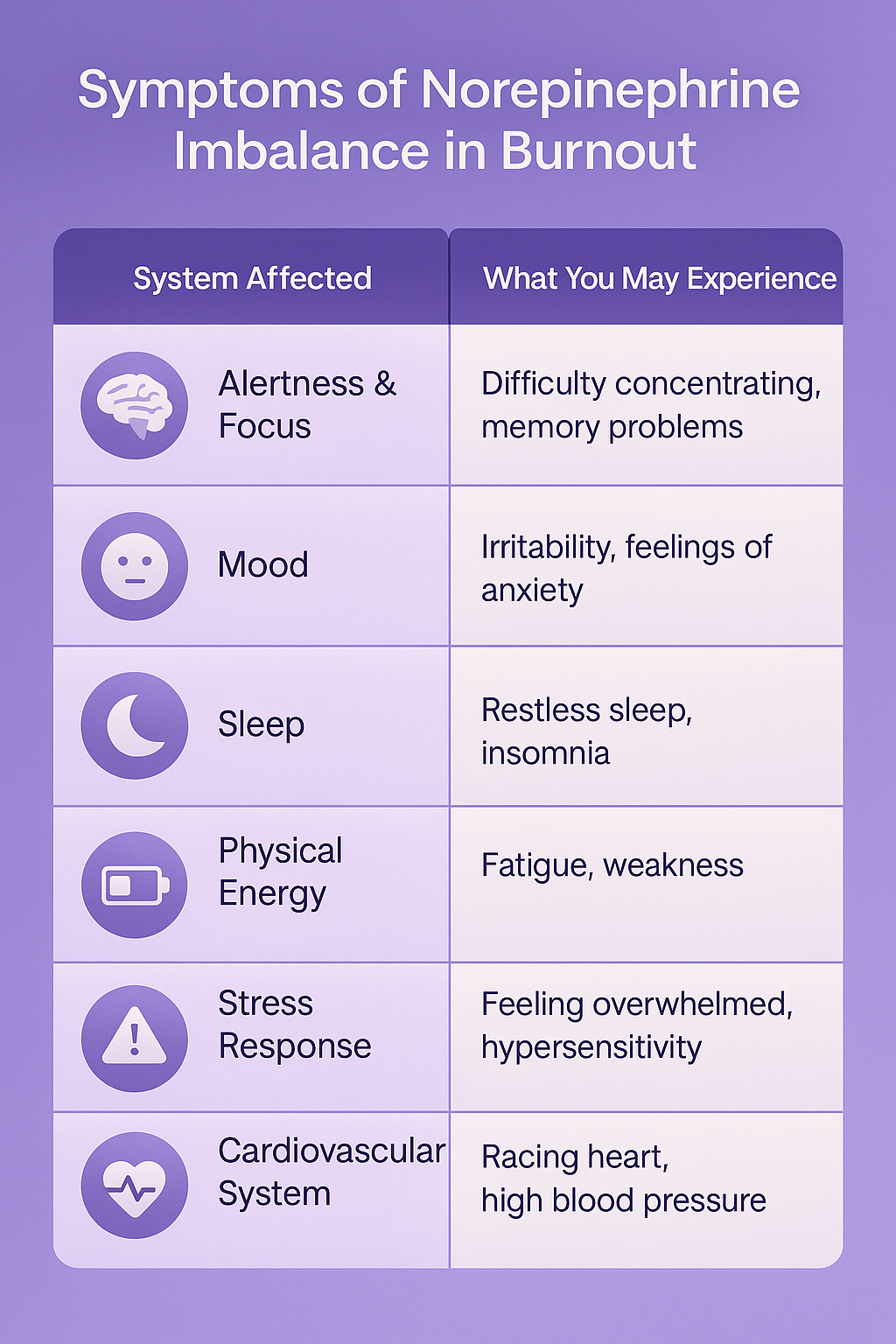
Symptoms of Norepinephrine Imbalance in Burnout
A norepinephrine imbalance may also cause headaches, dizziness, digestive problems, and sensitivity to light or sound.
Why Norepinephrine Matters in Burnout
In moderation, norepinephrine is a life-saver. It helps you perform under pressure, focus intensely, and react quickly. But chronic overexposure wears out your nervous system.
This leads to the familiar "wired but tired" feeling so common in burnout:
Too alert to relax
Too exhausted to function at full capacity
Without intervention, this cycle can worsen into long-term anxiety disorders, depression, or chronic fatigue syndrome.
Research has shown that burnout-induced norepinephrine dysregulation also reduces levels of other neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, worsening emotional and cognitive symptoms.
The Locus Coeruleus: The Epicenter of Norepinephrine Activity
The locus coeruleus acts as the brain’s norepinephrine hub. It has widespread projections to the prefrontal cortex (attention), amygdala (emotion), hippocampus (memory), and spinal cord (motor control).
In burnout, the locus coeruleus fires excessively, disrupting the balance of focus and rest. Over time, it leads to:
Cognitive fatigue
Emotional hypersensitivity
Memory difficulties
Reduced decision-making ability
Can You Reset Your Norepinephrine System?
Yes. The human brain is adaptable. Your norepinephrine system can stabilize with the right approach:
1. Activate the Parasympathetic Nervous System
Practice deep breathing, meditation, or gentle yoga.
Engage in progressive muscle relaxation.
Use EEG-guided relaxation tools like MelodiaSync to calm the overactive stress response.
2. Improve Sleep Hygiene
Go to bed and wake up at consistent times.
Avoid screens, caffeine, and alcohol before bedtime.
Use blackout curtains and white noise to improve sleep quality.
3. Engage in Aerobic Exercise
Moderate-intensity cardio helps regulate norepinephrine levels.
Activities like walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing are highly effective.
4. Reduce Exposure to Chronic Stressors
Set healthy work-life boundaries.
Take frequent breaks during the day.
Practice mindfulness to stay grounded.
5. Nutrition and Hydration
Eat a balanced diet rich in omega-3s, antioxidants, and magnesium.
Stay hydrated to support overall brain function.
How MelodiaSync Can Help
MelodiaSync’s EEG-guided sound programs are designed to:
Lower the brain’s overactive stress response
Promote calm and balanced neural activity
Help you re-establish a healthy circadian rhythm
By stimulating relaxation pathways, MelodiaSync helps regulate norepinephrine levels, easing the "wired but tired" pattern and promoting emotional resilience.
Finding Balance Again
Burnout overloads your norepinephrine system, turning it from a helpful signal into a harmful force. Understanding this allows you to take actionable steps to reset your brain chemistry.
Recovery takes time, but with supportive tools like MelodiaSync, lifestyle changes, and compassionate self-care, you can regain focus, energy, and emotional stability.
Your brain deserves balance, and recovery is possible.
If you’ve experienced burnout symptoms, know that you’re not alone. There is a path back to feeling calm, clear, and capable once again.
Disclaimer: This blog post is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for any medical concerns or treatment decisions.